A cybersecurity audit is intended to be a thorough examination and study of your company's infrastructure,” said Stephen Cobb, a senior security researcher at ESET, a cybersecurity company. “In part, it provides an objective and independent review of your organization’s strengths and weaknesses, so that you are fully aware of how to approach and address them.
What is a Cybersecurity audit?
A cybersecurity audit is intended to be a thorough examination and study of your company's infrastructure. It detects threats and vulnerabilities, revealing flaws and high-risk activities.
These audits assist firms in verifying what is on their network, what needs to be protected, and what gaps exist in their existing defenses so that updates may be made.
Deloitte also agrees that
Internal audit plays an important role in assisting organizations in their ongoing battle to manage cyber threats, both by providing an independent assessment of existing and required controls and by assisting the audit committee and board in understanding and addressing the diverse risks of the digital world.
Types of Cybersecurity audit
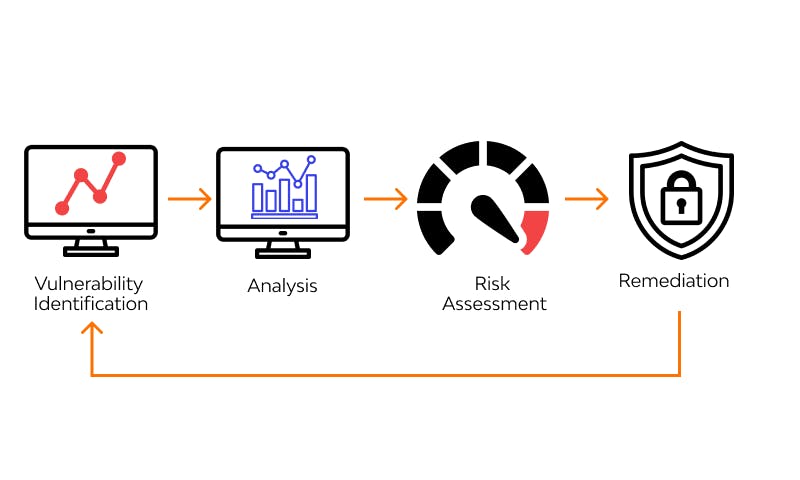
Risk assessment
The risk assessment process analyzes the various information assets that could be affected by a cyberattack (such as hardware, systems, laptops, customer data, and intellectual property) and then determines the various threats that could harm those assets. The image below shows the steps in Risk assessment.

Vulnerability assessment
A vulnerability assessment is a thorough examination of a system's security flaws. It determines whether the system is vulnerable to any known vulnerabilities, provides severity levels for those security breaches, and suggests patches or mitigation as needed.
Types of Vulnerability assessment
Network-based scans
Host-based scans
Wireless scans
Application scans
Database scans
These scans prevent threats ranging from:
SQL injection, XSS, and other code injection attacks.
Privilege escalation as a result of improper authentication procedures
Insecure defaults – software that comes pre-installed with insecure options, such as Passwords for admins that are easy to guess
Penetration testing
Penetration testing (or Pentesting) is an exercise that attempts to find and exploit vulnerabilities in a computer system. The goal of this simulated attack is to find any weak points in a system's security that attackers could exploit.
These flaws can be found in operating systems, services, and applications, as well as in incorrect configurations and unsafe end-user behavior. These evaluations can also be used to validate the effectiveness of defensive measures and end-user compliance with security regulations.
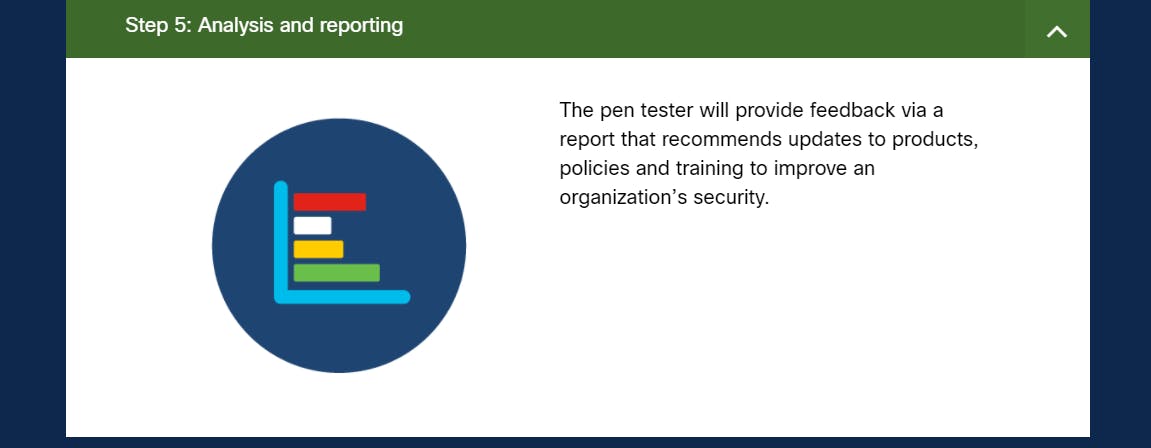
These are five stages of Penetration testing:
- Planning

- Scanning

- Gaining Access

- Maintaining Access

- Analysis and reporting
Compliance audit
Cybersecurity audits are used to determine compliance. According to SecurityScorecard, agencies that undertake a cybersecurity audit will "be able to determine whether or not they have the right security procedures in place while also ensuring they are in compliance with relevant rules."
Benefits of Cybersecurity audit
Highlight and address flaws
Provides an in-depth examination of internal and external security measures.
Identify weak points in your defense.
Determines whether or not you need to improve your security infrastructure.
Recommends how to use technology to improve enterprise security.
Keeping a step ahead of hackers
Reputation
Employee, client, and vendor assurance
Enhanced technological and security performance
Internal or External auditors
External auditors utilize a variety of software tools to identify flaws in your security systems. External auditors are highly skilled specialists who are not inexpensive. Internal audits, on the other hand, are less expensive, easier to handle, and allow businesses to acquire data and set their benchmarks in the auditing process. However, internal auditing can introduce bias into the auditing process; as a result, many audit committees and boards have established expectations for internal audits to recognize and assess potential risks. You choose.

